 |
| November 27, 2012 | Volume 08 Issue 44 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
Extend your range of motion: Controllers for mini motors
 FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
FAULHABER has added another extremely compact Motion Controller without housing to its product range. The new MC3603 controller is ideal for integration in equipment manufacturing and medical tech applications. With 36 V and 3 A (peak current 9 A), it covers the power range up to 100 W and is suitable for DC motors with encoder, brushless drives, or linear motors.
Learn more.
When is a frameless brushless DC motor the right choice?
 Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
Frameless BLDC motors fit easily into small, compact machines that require high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, such as robotic applications where a mix of low weight and inertia is critical. Learn from the experts at SDP/SI how these motors can replace heavier, less efficient hydraulic components by decreasing operating and maintenance costs. These motors are also more environmentally friendly than others.
View the video.
Tiny and smart: Step motor with closed-loop control
 Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Nanotec's new PD1-C step motor features an integrated controller and absolute encoder with closed-loop control. With a flange size of merely 28 mm (NEMA 11), this compact motor reaches a max holding torque of 18 Ncm and a peak current of 3 A. Three motor versions are available: IP20 protection, IP65 protection, and a motor with open housing that can be modified with custom connectors. Ideal for applications with space constraints, effectively reducing both wiring complexity and installation costs.
Learn more.
Closed loop steppers drive new motion control applications
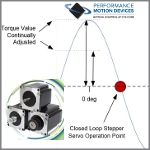 According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
According to the motion experts at Performance Motion Devices, when it comes to step motors, the drive technique called closed loop stepper is making everything old new again and driving a burst of interest in the use of two-phase step motors. It's "winning back machine designers who may have relegated step motors to the category of low cost but low performance."
Read this informative Performance Motion Devices article.
Intelligent compact drives with extended fieldbus options
 The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
The intelligent PD6 compact drives from Nanotec are now available with Profinet and EtherNet/IP. They combine motor, controller, and encoder in a space-saving package. With its 80-mm flange and a rated power of 942 W, the PD6-EB is the most powerful brushless DC motor of this product family. The stepper motor version has an 86-mm flange (NEMA 34) and a holding torque up to 10 Nm. Features include acceleration feed forward and jerk-limited ramps. Reduced installation time and wiring make the PD6 series a highly profitable choice for machine tools, packaging machines, or conveyor belts.
Learn more.
NASA making steady progress on developing robotic satellite servicing capabilities
By Bob Granath, NASA's John F. Kennedy Space Center
With satellites playing increasingly important roles in everyday life, NASA is developing the technology to build Earth-orbiting, roving "service stations" capable of extending the life of these spacecraft. Engineers at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida are assisting the space agency's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, in developing the concept for bringing a high-technology gas pump, robotic mechanic, and tow truck to satellites in space.

This artist's concept shows a servicing spacecraft, left, approaching a satellite needing assistance. NASA is developing technology needed to bring a high-technology "gas pump, robotic mechanic, and tow truck" to satellites in orbit. [Image credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center]
There are 149 government-owned spacecraft and 275 commercial satellites currently in geosynchronous Earth orbit, or GEO, around the Earth. Placed 22,300 miles above the Earth, these satellites play key roles in communications, science, defense, and weather monitoring. GEO permits these spacecraft essentially to stay over the same point, allowing for constant coverage of a designated position. This is crucial for satellites relaying meteorology and television signals covering specific portions of the globe.
According to Tom Aranyos, technical integration manager in NASA's Fluids and Propulsion Division at Kennedy, engineers at the Florida spaceport are supporting the hypergolic propellant refueling portion of the Goddard-led study examining how free-flying servicing spacecraft could expand options in orbit for government and commercial satellite owners.
"America depends on satellites in geosynchronous orbit," said Aranyos. "These expensive spacecraft eventually develop systems failures or run out of propellant. Servicing and refueling these satellites can keep them operating longer and in the correct orbit, giving the nation and their owners more value for their investment."
Preliminary work with a technology demonstrator is underway on the International Space Station. The crew of space shuttle Atlantis' STS-135 flight delivered the Robotic Refueling Mission, or RRM, hardware to the station in July 2011.
During a spacewalk, astronauts Mike Fossum and Ron Garan transferred the RRM onto a temporary platform on the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, also known as Dextre, a two-armed robot developed by the Canadian Space Agency that serves as part of the station's Mobile Servicing System. RRM now resides on the Express Logistics Carrier 4 platform outside the station.
Designed by the same team that developed the instruments and astronaut tools for the Hubble Space Telescope servicing missions, the four RRM tools cut and manipulate wires, unscrew caps, open and close valves, and transfer fluid, demonstrating that a remote-controlled robot can service and refuel a satellite in orbit. In March 2012, the 12-ft Dextre performed the most intricate operation ever attempted by a space robot: cutting two twisted "lock wires," each 20 thousandths of an inch (0.5 mm) in diameter using the RRM Wire Cutter Tool. The RRM refueling demonstration is scheduled to take place on the space station by the end of 2012. Meanwhile, back on the ground, preparations are ramping up for a second set of activities and task boards to continue RRM operations through 2014.
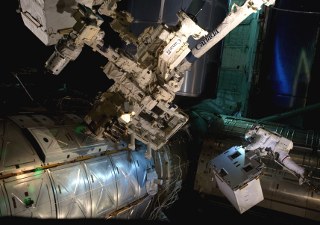
With his feet secured on a restraint on the space station remote manipulator system's robotic arm, NASA astronaut Mike Fossum holds the Robotics Refueling Mission payload. The four tools on the test device cut and manipulated wires, unscrewed caps, opened and closed valves, and transferred fluid, demonstrating that a remote-controlled robot can service and refuel a satellite. [Photo credit: NASA]
Goddard's study and associated development campaign to advance Technology Readiness Levels, or TRLs, of satellite-servicing technologies are the next steps in building capabilities for a fully robotic maintenance vehicle that could service satellites, including those that were not originally intended to be serviced.
Goddard envisions a future in which servicer spacecraft equipped with a state-of-the-art navigation system, enhanced robotic arms and tools, and a supply of propellant would be able to autonomously rendezvous and dock with a satellite needing aid. Depending on the type of assistance needed, the servicing spacecraft could perform one of five "R" capabilities: refueling, repositioning, remote survey, component replacement, or repairing an ailing satellite. The Goddard development campaign is designed to ensure that the capabilities and technologies are matured, vetted, and ready for potential future servicing missions.
"Kennedy, as part of the Goddard team, is studying and performing preliminary tests for the design, development, and qualification testing of the critical subsystem for an in-orbit hypergolic propellant transfer system," said Aranyos, who is leading Kennedy's technical team for the project. "That will include a pumping system with high metering accuracy and hose management system to transfer propellant to multiple client locations on existing orbiting satellites."
Since May 2011, Aranyos' technical team has been developing a highly reliable, leak-free hypergolic propellant transfer module capable of high-accuracy metering at high-pressure, low-flow rates. Hypergolic propellants such as nitrogen tetroxide, hydrazine, and monomethyl hydrazine are the propellants most frequently used in satellites.
A key milestone in the Kennedy effort was completed in August with testing of the low-TRL "proof of concept" pump led by Brian Nufer who leads the propulsion subsystem team. NASA engineers worked with technicians from Sierra Lobo of Fremont, OH, under an institutional support contract to conduct the first simulation of proof-of-concept hardware to see how to pump highly corrosive, toxic, low-viscosity (low-thickness), and high-density nitrogen tetroxide propellant at required transfer pressures.
"The operation was highly successful in that it showed that the experimental system worked as designed," Aranyos said. "It provided the engineering team with an enormous amount of performance data to better understand how the pump operates and provide lessons learned to be incorporated to the flight pump fabrication and operating procedures."
In the near future, Kennedy's engineering team will design and perform functional risk-reduction tests on a propellant transfer module similar to a flight-like unit.
"It will be a full-scale engineering development unit," Aranyos said. "The propellant hose-management system, which completed initial proof-of-concept testing in May 2012 led by Erik Tormoen of NASA's Launch Vehicle Electrical Systems Branch, is planning engineering development unit testing for the second quarter of fiscal year 2013."
Aranyos is pleased with the progress so far.
"This is a great partnership with Goddard," he said. "Through most of Kennedy's history, we have received, processed, and launched vehicles developed at other centers. Over our 50-year history, we've developed an extensive knowledge base and diverse capabilities. Projects such as this give us an opportunity to put that expertise to work."
Published November 2012
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

